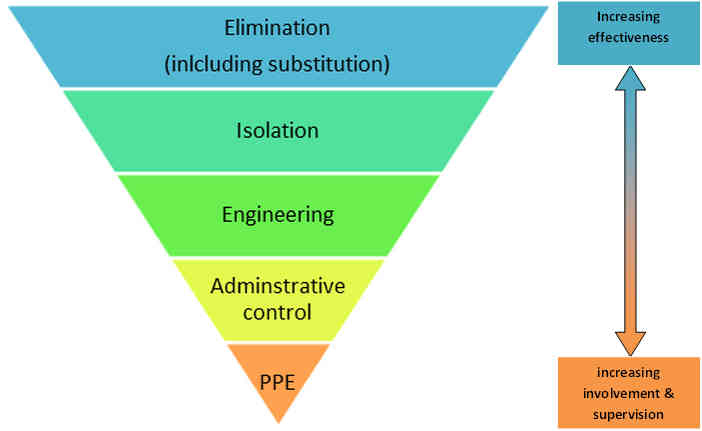
Corrosion associate risk is controlled by using a predetermined hierarchy of engineering control. The primary aim of risk control is to eliminate the corrosion risk and the best way is to remove the corrosion hazard. If this is not possible or impractical, then the corrosion risk must be minimised by other level of control options in this hierarchy.
- Elimination
This is the most preferable and most effective in hazards control. The control either remove hazard or replace it with a less hazardous one. For example, removal of unnecessary thermal insulation in the equipment may eliminate corrosion under insulation; Replace of carbon steel pipe with HDPE pipe may eliminate the corrosion issue in gathering system.
- Isolation
Restricting access to equipment therefore the hazard is not going to occur easily. The good example of this is coating application which restricted the access of oxygen/moisture to bare metal surface.
- Engineering controls
If the hazard cannot be eliminated or a safer substitute cannot be found, the next best approach is to used engineering controls. The basic types of engineering controls in corrosion management is process control. Cathodic protection is a good example of engineering control to mitigate external corrosion of buried pipeline.
- Administrative controls
Administrative control is by applying established management plan, standard operation procedure and appropriate training programme to manage the corrosion.
The available corrosion controls are summarised in the following table.
| Control hierarchy | Controls |
|---|---|
| Elimination (including Substitution) |
|
| Isolation |
|
|
Engineering |
|
| Administrative control |
|