Principle of Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
A magnetic flux leakage (MFL) inspection is the type of in-line inspection technology in which a magnetic saturation is induced in the pipe wall between two poles of a permanent strong magnet. The pipe wall is magnetised by using this magnet. Anomalies affect the distribution of the magnetic flux in the wall, by which it is used to detect and characterize anomalies accordingly. Any metal-loss in the pipe wall will cause the induced magnetic flux leakage, which can be monitored using a detector and hence metal-loss defects can be identified and sized. MFL can be utilised by both liquid and gas pipelines. 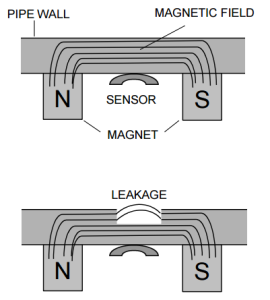
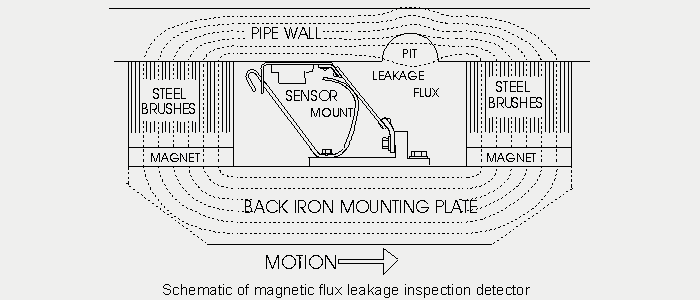
Axial MFL Tool Detection

Axial MFL Tool
Depending on the layout of magnets, the permanent magnetic field can either be axial or circumferential. For the circumferential MFL, it is best for detecting and sizing the defects orientated along the pipeline axial direction. For axial MFL, it is best for detecting and sizing the circumferential defects, such as circumferential slotting and grooving. Therefore, the understanding of major flaw type is critical for the MFL tool selection.
MFL Application and Limitation

Circumferential MFL Tool
MFL is considered as a metal loss tool since significant of leakage is required for the detection. NACE SP 0102 has outlined the anomalies and features are likely to be detected by MFL.
Table 1 Guideline of MFL for pipeline anomalies detection (NACE SP 0102)
| Anomaly | Imperfection/Defect/Features | Standard resolution MFL | High resolution MFL |
| Metal loss | External corrosion | Detection
Sizing |
Detection
Sizing |
| Internal Corrosion | Detection
Sizing |
Detection
Sizing |
|
| Gouging | Detection
Sizing |
Detection
Sizing |
|
| Crack-Like Anomalies | Narrow Axial External Corrosion | Detection | Detection |
| Stress Corrosion Cracking | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Fatigue Cracks | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Long Seam Cracks, etc. (toe cracks, hook cracks, incomplete fusion, preferential seam corrosion) | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Circumferential Cracks | No Detection | Detection
Sizing |
|
| Hydrogen-Induced Cracking (HIC) | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Deformation | Sharp Dents | Detection | Detection |
| Flat Dents | Detection | Detection | |
| Buckles | Detection | Detection | |
| Wrinkles, Ripples | Detection | Detection | |
| Ovalities | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Misc. Components |
In-Line Valves and Fittings | Detection | Detection |
| Casings (Concentric) | Detection | Detection | |
| Casings (Eccentric) | Detection | Detection | |
| Bends | Limited detection | Limited detection | |
| Branch Appurtenances/Hot Taps |
Detection | Detection | |
| Close Metal Objects | Detection | Detection | |
| Thermite Welds | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Pipeline Coordinates | No Detection | Detection | |
| Previous Repairs |
Type A Repair Sleeve | Detection | Detection |
| Composite Sleeve | Detection | Detection | |
| Type B Repair Sleeve | Detection | Detection | |
| Patches/Half Soles | Detection | Detection | |
| Puddle Welds | Limited detection | Limited detection | |
| Misc. Damage |
Laminations | Limited detection | Limited detection |
| Inclusions (Lack of Fusion) | Limited detection | Limited detection | |
| Cold Work | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Hard Spots | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Grind Marks | Limited detection | Limited detection | |
| Strain | No Detection | No Detection | |
| Girth Weld Anomaly(voids, etc.) | Limited detection | Detection | |
| Scabs/Slivers/Blisters | Limited detection | Limited detection |
Reference
NACE SP0102 In-Line Inspection of Pipelines
M Orazem, Underground Pipeline Corrosion, Woodhead Publishing
Lloyd Pirtle, An Update of ILI Tools & Other Industry Technologies for the Oklahoma Gas Association, August 27th, 2013
In-Line Inspection Tools for Pipelines

