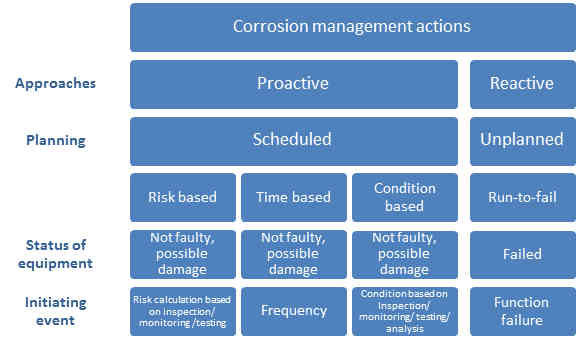
There are different types of corrosion management strategy, namely proactive or reactive approaches. In practical, both approaches are used in operators’ corrosion management practice. In general, reactive approach is the least cost effective option when the maintenance requirements are intensive. The operators strive to optimise the balance between cost, compliance and safe operation.
• Risk based strategy
Risk based strategy is going to be the main strategy for operators’ corrosion management for cost saving purpose. Once risk level is known, i.e. risk baseline, risk probability and consequence are established, the monitoring, inspection and mitigation will be easily managed by risk based strategy. API RP580 Risk-Based Inspection provides guideline on risk based strategy. API RP581 Risk-Based Inspection Technology provides a tool to quantify the risk.
• Time based strategy
Time based strategy is a strategy to manage the corrosion related activities in predefined time intervals. Some standard and operators still prefers time based strategy as the primary corrosion management strategy. Time based strategy is still widely adopted in corrosion monitoring, sampling testing and inspection activities. However, the biggest challenge for time based strategy is cost and resource demanding. Automobile log book service by time schedule is a typical example of time based strategy. AS/NZS 3788 Pressure equipment – In-service inspection, is a time based inspection strategy, which specifies the minimum inspection interval for different type of static equipment.
• Condition based strategy
Condition-based strategy is a strategy based on the corrosion related failure indicators. The strategy is more used in rotatory equipment. The challenge for condition based strategy is to establish the failure indicators for different types of equipment under the service condition. The maintenance, repair or replacement is performed after one or more indicators show that equipment is going to fail.
• Run-to-fail strategy
This strategy will be used in over-design case, e.g. if the corrosion allowance is sufficient to compensate any erosion/corrosion in the life span of the equipment, or little corrosion or other mechanical failure mechanisms to be expected.