Stray Current Corrosion of Ductile Iron Pipe (DIP) Near Steel Pipeline
The most notorious incidents is catastrophe of Guadalajara Sewer Explosion.The sewer network in Guadalajara, Mexico was exploded in April 1992. The official toll was: 206 dead, 500 to 600 missing, 1 800 injured and, in all, 4 500 disaster victims. Associations estimate that the catastrophe actually caused at least 1000 deaths. The catastrophe caused damage worth 200 billion pesos (76 million Euros 2006), which included ~13 km of streets, 1500 houses, 1224 buildings and 637 vehicles.

Corrosion damaged pipeline and DIP in 1992 Guadalajara catastroph
The scientific investigation found the stray current corrosion is the blame. According to the report,
- There is water pipe which is zinc coated ductile iron pipe (DIP) installed around the 12 inch high pressure gasoline pipeline. This DIP is in the proximity of the gasoline.
- Gasoline pipeline is under cathodic protection.
- Gasoline pipeline had two holes within a cavity and an eroded area, all in a longitudinal direction. The first hole penetrate the whole wall thickness of the gasoline pipeline, while the second hole in gasoline pipelines did not perforate the internal wall.
- DIP line has a hole, this hole coincides with holes in gasoline pipe.
The investigators believed the water galvanized pipe had suffered stray current corrosion effects due to visible in pits of different sizes. The DIP pick up the current which was designed to protect the gasoline pipeline. When this stray current leaving the DIP and returning to soil/gasoline pipeline, this caused the severe metal loss of DIP. After DIP loss the containment, flow accelerated corrosion is caused by gushed water. This gushed water further aggravated the corrosion environments around the gasoline pipeline. Nevertheless, this ductile iron pipe may also prevent the cathodic protection current reaching to the gasoline pipeline surface locally, which is termed as CP shielding effect. The subsequent corrosion of the gasoline pipeline, in turn, caused leakage of gasoline into a main sewer line.
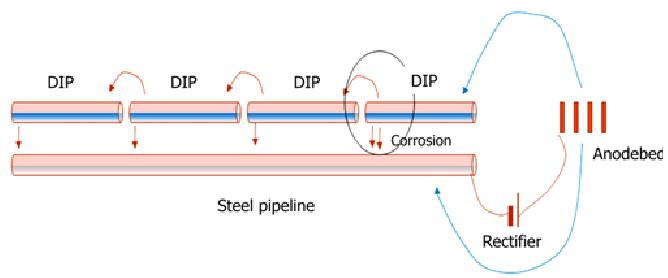
Stray current corrosion in DIP near steel pipeline
Just recently, Li and Kim simulated the effect of stray current on ductile iron pipe near cathodically protected steel pipeline. The results agreed with finding of the previous investigation. Li and Kim found that When all joints in DIP were electrically connected, the maximum corrosion rate was 0.005 mm/y. However, when the joints were isolated, the corrosion rate increased due to the jumping effect of stray current at isolated joints, which resulted in the increase of maximum corrosion rate to 0.87 mm/y.
The authors also believed the best way to reduce stray current corrosion of DIP is the proactive application of control methods from the design stage, which include the increase of anode bed and the pipe distance, electrical connection of DIP joints, installation of sacrificial anode at isolated joints, or the application of CP on DIP.
Reference:
Ministry in charge of the environment – DPPR / SEI / BARPI No 3543
Malo JM, Salinas V, Uruchurtu J. Stray Current Corrosion Causes Gasoline Pipeline Failure. Materials Performance 1994; 33: 63
Li SY, Kim YG Numerical Modelling of Stray Current Corrosion of Ductile Iron Pipe Induced By Foreign Cathodic Protection System, Metals and Materials International 2013, 19: 717
Seconds From Disaster S01E08 Inferno In Guadalajara National Geographic Channel. 2004


Pingback: DC STRAY CURRENT ANALYSIS AND MITIGATION - Corrosion and Corrosion Control
I’ve read a few good stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much attempt you place to create this type of great informative website.|
Hello to every body, it’s my first visit of this webpage; this weblog contains awesome and in fact excellent stuff in favor of readers.|
That really caturpes the spirit of it. Thanks for posting.